Literacy Strategies in the Classroom
Vocabulary
Our subject leaders ensure that vital vocabulary, including tier 2 and tier 3 words, are planned for, and are taught at carefully sequenced points across their curricula.
Vocabulary is foregrounded in our lessons and a consistent approach is taken to explicitly teach the words that will allow students to access the lesson and speak like a subject expert. Every lesson follows the same rigorous structure using a template which provides the definition, shows how to use the word in a sentence and a memory clue (usually an image or etymology). Teachers model the correct pronunciation of the words and students repeat the words in a choral response; this supports spelling and builds students’ confidence when using the words. Teachers might break down words into syllables or discuss phonemes where necessary.
| Key Vocabulary | Definition | Context | Memory Clue |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Sophisticated |
Having or showing knowledge and experience |
We select sophisticated vocabulary when we are writing in lessons. |
Sophos - wise/ clever |
To ensure that students understand the words and interact with the new vocabulary, we use multiple-choice questions to further develop students’ understanding of the new vocabulary. The questions might explore the correct use of words in a sentence or a context, similar/ different words or link the vocabulary to existing knowledge. This provides some of the 14–20 interactions that research suggests are vital for embedding the word within our long-term memories.
Students are then expected and encouraged to use this upgraded vocabulary in their verbal and written responses throughout the lesson.
This vocabulary will be retrieved in future lessons through 'Do Now' activities.
Frayer Models
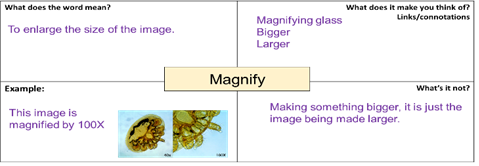
Frayer Models are used to delve deeper into the meanings of words.

Here are some examples from Science and English.

KIM Models
These are Knowledge, Information and Memory clues, which provide visual glossaries to help us retrieve the meaning of keywords.
|
Knowledge: |
Information: |
Memory Clue: |
|
contrast |
very different from |
|
Word Walls
We use word walls to visually store keywords so that students can come back to these, and we can ensure that the words are retained. This acts as a growing word bank for our students that they can keep coming back to.
Reading in the Classroom
Our teachers are trained in our whole-school reading and disciplinary literacy strategies and play a crucial role in developing students' comprehension and disciplinary literacy skills.
Reading is completed in a variety of ways for different purposes; teachers use a mixture of independent reading, students’ reading aloud and teacher modelling of fluent reading to suit the group, text and purpose.
Middle leaders have embedded reading into their curriculum to ensure that students understand the vital role that reading plays in learning. We have a school structure for scaffolding and planning reading activities that is adapted to support disciplinary reading across the school.
Some of the supportive strategies that teachers use are:
- Dual coding
- ‘Chunking’ the text
- Reading the text aloud using expert fluency
- Using questioning to support understanding
We want students to read strategically across the curriculum. Therefore, we have provided a clear model of how we teach reading:
|
Before |
During |
After |
|
How we read
Knowing the purpose of our reading
|
|
 The red apple contrasts with the green background.
The red apple contrasts with the green background.